
2704N
EN Table Saw INSTRUCTION MANUAL 9
PL STOŁOWA PILARKA
TARCZOWA INSTRUKCJA OBSŁUGI 18
HU Asztali fűrész HASZNÁLATI KÉZIKÖNYV 28
SK Stolová píla NÁVOD NA OBSLUHU 37
CS Stolní okružní pila NÁVOD K OBSLUZE 46
UK Настільний
розпилювальний верстат ІНСТРУКЦІЯ З
ЕКСПЛУАТАЦІЇ 55
RO Ferăstrău de masă MANUAL DE INSTRUCŢIUNI 65
DE Tischkreissäge BETRIEBSANLEITUNG 74

620 mm
1
525 mm
Fig.1
1
25 mm
2
Fig.2
12
Fig.3
1
Fig.4
1
2
3
Fig.5
12
Fig.6
1
Fig.7
12
3
Fig.8
2

12
Fig.9
(A)
(B)
90
90 45
45
Fig.10
1
Fig.11
1
Fig.12
12 34
Fig.13
3
4
2
12
1
2
Fig.14
1
Fig.15
3

1
Fig.16
1
2
Fig.17
2
12
Fig.18
1
1
2
Fig.19
21
Fig.20
1
32
Fig.21
12
3
45
Fig.22
1
2
Fig.23
4

12
3
Fig.24
12
3
4
5
Fig.25
1
2
3
Fig.26
12
3
3
Fig.27
1
A
B
Fig.28
1
Fig.29
Fig.30
123
4
Fig.31
5

12
34
Fig.32
1
2
Fig.33
Fig.34
120mm
300mm
130mm
50mm
6mm
300mm
130mm
100mm
50mm
9.5mm
50mm
8mm
1
2
3
4
Fig.35
9.5mm 19mm 120mm
40mm
140mm
460mm
1
Fig.36
Fig.37
6

Fig.38
1
Fig.39
Fig.40
1
2
Fig.41
12
34
Fig.42
2
3
1
Fig.43
1
3
2
Fig.44
1
Fig.45
7

Fig.46
1
Fig.47
1
23
Fig.48
Fig.49
1
23
Fig.50
8

9ENGLISH
ENGLISH (Original instructions)
SPECIFICATIONS
Model: 2704N
Arbor hole
(Country specic) 30 mm / 25.4 mm
Blade diameter 260 mm
Max. cutting capacities bevel 0° 93 mm
bevel 45° 64 mm
No load speed 5,200 min-1
Table size (L x W) with sub tables (R) and (back) 1,045 mm x 1,066 mm (tables extended)
665 mm x 753 mm (tables stored)
with sub table (R)
without sub table (back) 567 mm x 1,066 mm (table extended)
567 mm x 753 mm (table stored)
Dimensions (L x W x H) with
table(s) not extended with sub tables (R) and (back) 715 mm x 753 mm x 483mm
with sub table (R)
without sub table (back) 665 mm x 753 mm x 483 mm
Net weight 35.2 kg - 37.0 kg
Safety class /II
• Due to our continuing program of research and development, the specications herein are subject to change
without notice.
• Specications may differ from country to country.
• The weight may differ depending on the attachment(s). The lightest and heaviest combination, according to
EPTA-Procedure 01/2014, are shown in the table.
Symbols
The following show the symbols used for the equip-
ment. Be sure that you understand their meaning before
use.
Read instruction manual.
DOUBLE INSULATION
Wear safety glasses.
Do not place hand or ngers close to the
blade.
Only for EU countries
Do not dispose of electric equipment
together with household waste material! In
observance of the European Directive, on
Waste Electric and Electronic Equipment
and its implementation in accordance with
national law, electric equipment that have
reached the end of their life must be col-
lected separately and returned to an envi-
ronmentally compatible recycling facility.
Intended use
The tool is intended for cutting in wood.
Straight cutting, bevel cutting, and miter cutting are
available with this tool. This tool is not designed for non-
through cutting.
Power supply
The tool should be connected only to a power supply of
the same voltage as indicated on the nameplate, and
can only be operated on single-phase AC supply. They
are double-insulated and can, therefore, also be used
from sockets without earth wire.
Noise
The typical A-weighted noise level determined accord-
ing to EN62841:
Sound pressure level (LpA) : 94 dB(A)
Sound power level (LWA) : 107 dB (A)
Uncertainty (K) : 3 dB(A)
WARNING: Wear ear protection.
EC Declaration of Conformity
For European countries only
The EC declaration of conformity is included as Annex A
to this instruction manual.

10 ENGLISH
SAFETY WARNINGS
General power tool safety warnings
WARNING: Read all safety warnings, instruc-
tions, illustrations and specications provided
with this power tool. Failure to follow all instructions
listed below may result in electric shock, re and/or
serious injury.
Save all warnings and instruc-
tions for future reference.
The term "power tool" in the warnings refers to your
mains-operated (corded) power tool or battery-operated
(cordless) power tool.
Safety instructions for table saws
Guarding related warnings
1. Keep guards in place. Guards must be in work-
ing order and be properly mounted. A guard
that is loose, damaged, or is not functioning cor-
rectly must be repaired or replaced.
2.
Make sure the saw blade is not contacting the
guard, riving knife or the workpiece before the
switch is turned on. Inadvertent contact of these items
with the saw blade could cause a hazardous condition.
3. Adjust the riving knife as described in this
instruction manual. Incorrect spacing, position-
ing and alignment can make the riving knife inef-
fective in reducing the likelihood of kickback.
4.
For the riving knife and anti-kickback pawls to
work, they must be engaged in the workpiece.
The riving knife and anti-kickback pawls are ineffec-
tive when cutting workpieces that are too short to
be engaged with the riving knife and anti-kickback
pawls. Under these conditions a kickback cannot be
prevented by the riving knife and antikickback pawls.
5. Use the appropriate saw blade for the riving
knife. For the riving knife to function properly, the
saw blade diameter must match the appropriate
riving knife and the body of the saw blade must be
thinner than the thickness of the riving knife and
the cutting width of the saw blade must be wider
than the thickness of the riving knife.
Cutting procedures warnings
1. DANGER: Never place your ngers or
hands in the vicinity or in line with the saw
blade. A moment of inattention or a slip could
direct your hand towards the saw blade and result
in serious personal injury.
2.
Feed the workpiece into the saw blade only
against the direction of rotation. Feeding the
workpiece in the same direction that the saw blade is
rotating above the table may result in the workpiece,
and your hand, being pulled into the saw blade.
3.
Never use the mitre gauge to feed the workpiece
when ripping and do not use the rip fence as a
length stop when cross cutting with the mitre
gauge. Guiding the workpiece with the rip fence
and the mitre gauge at the same time increases the
likelihood of saw blade binding and kickback.
4.
When ripping, always apply the workpiece feed-
ing force between the fence and the saw blade.
Use a push stick when the distance between the
fence and the saw blade is less than 150 mm,
and use a push block when this distance is less
than 50 mm. “Work helping” devices will keep your
hand at a safe distance from the saw blade.
5. Use only the push stick provided by the manu-
facturer or constructed in accordance with the
instructions. This push stick provides sufcient
distance of the hand from the saw blade.
6. Never use a damaged or cut push stick. A
damaged push stick may break causing your hand
to slip into the saw blade.
7.
Do not perform any operation “freehand”. Always
use either the rip fence or the mitre gauge to posi-
tion and guide the workpiece. “Freehand” means
using your hands to support or guide the workpiece,
in lieu of a rip fence or mitre gauge. Freehand sawing
leads to misalignment, binding and kickback.
8. Never reach around or over a rotating saw
blade. Reaching for a workpiece may lead to
accidental contact with the moving saw blade.
9. Provide auxiliary workpiece support to the rear
and/or sides of the saw table for long and/or
wide workpieces to keep them level. A long and/
or wide workpiece has a tendency to pivot on the
table’s edge, causing loss of control, saw blade
binding and kickback.
10. Feed workpiece at an even pace. Do not bend
or twist the workpiece. If jamming occurs, turn
the tool off immediately, unplug the tool then
clear the jam. Jamming the saw blade by the
workpiece can cause kickback or stall the motor.
11. Do not remove pieces of cut-off material while
the saw is running. The material may become
trapped between the fence or inside the saw blade
guard and the saw blade pulling your ngers into
the saw blade. Turn the saw off and wait until the
saw blade stops before removing material.
12. Use an auxiliary fence in contact with the table
top when ripping workpieces less than 2 mm
thick. A thin workpiece may wedge under the rip
fence and create a kickback.
Kickback causes and related warnings
Kickback is a sudden reaction of the workpiece due to a
pinched, jammed saw blade or misaligned line of cut in
the workpiece with respect to the saw blade or when a
part of the workpiece binds between the saw blade and
the rip fence or other xed object.
Most frequently during kickback, the workpiece is lifted
from the table by the rear portion of the saw blade and
is propelled towards the operator.
Kickback is the result of saw misuse and/or incorrect
operating procedures or conditions and can be avoided
by taking proper precautions as given below.
1. Never stand directly in line with the saw blade.
Always position your body on the same side of
the saw blade as the fence. Kickback may propel
the workpiece at high velocity towards anyone
standing in front and in line with the saw blade.
2. Never reach over or in back of the saw blade
to pull or to support the workpiece. Accidental
contact with the saw blade may occur or kickback
may drag your ngers into the saw blade.

11 ENGLISH
3. Never hold and press the workpiece that is
being cut off against the rotating saw blade.
Pressing the workpiece being cut off against the
saw blade will create a binding condition and
kickback.
4. Align the fence to be parallel with the saw
blade. A misaligned fence will pinch the workpiece
against the saw blade and create kickback.
5. Use extra caution when making a cut into blind
areas of assembled workpieces. The protrud-
ing saw blade may cut objects that can cause
kickback.
6. Support large panels to minimise the risk of
saw blade pinching and kickback. Large panels
tend to sag under their own weight. Support(s)
must be placed under all portions of the panel
overhanging the table top.
7. Use extra caution when cutting a workpiece
that is twisted, knotted, warped or does not
have a straight edge to guide it with a mitre
gauge or along the fence. A warped, knotted,
or twisted workpiece is unstable and causes mis-
alignment of the kerf with the saw blade, binding
and kickback.
8. Never cut more than one workpiece, stacked
vertically or horizontally. The saw blade could
pick up one or more pieces and cause kickback.
9. When restarting the saw with the saw blade in
the workpiece, centre the saw blade in the kerf
so that the saw teeth are not engaged in the
material. If the saw blade binds, it may lift up the
workpiece and cause kickback when the saw is
restarted.
10. Keep saw blades clean, sharp, and with suf-
cient set. Never use warped saw blades or saw
blades with cracked or broken teeth. Sharp and
properly set saw blades minimise binding, stalling
and kickback.
Table saw operating procedure warnings
1. Turn off the table saw and disconnect the
power cord when removing the table insert,
changing the saw blade or making adjust-
ments to the riving knife, anti-kickback pawls
or saw blade guard, and when the machine
is left unattended. Precautionary measures will
avoid accidents.
2. Never leave the table saw running unattended.
Turn it off and don’t leave the tool until it
comes to a complete stop. An unattended run-
ning saw is an uncontrolled hazard.
3. Locate the table saw in a well-lit and level area
where you can maintain good footing and
balance. It should be installed in an area that
provides enough room to easily handle the
size of your workpiece. Cramped, dark areas,
and uneven slippery oors invite accidents.
4. Frequently clean and remove sawdust from
under the saw table and/or the dust collection
device. Accumulated sawdust is combustible and
may self-ignite.
5. The table saw must be secured. A table saw that
is not properly secured may move or tip over.
6. Remove tools, wood scraps, etc. from the table
before the table saw is turned on. Distraction or
a potential jam can be dangerous.
7. Always use saw blades with correct size and
shape (diamond versus round) of arbour
holes. Saw blades that do not match the mounting
hardware of the saw will run off-centre, causing
loss of control.
8. Never use damaged or incorrect saw blade
mounting means such as anges, saw blade
washers, bolts or nuts. These mounting means
were specially designed for your saw, for safe
operation and optimum performance.
9. Never stand on the table saw, do not use it as
a stepping stool. Serious injury could occur if the
tool is tipped or if the cutting tool is accidentally
contacted.
10. Make sure that the saw blade is installed to
rotate in the proper direction. Do not use
grinding wheels, wire brushes, or abrasive
wheels on a table saw. Improper saw blade
installation or use of accessories not recom-
mended may cause serious injury.
Additional instructions
1. Only use the saw blades that are marked with
a speed equal or higher than the speed marked
on the tool.
2. Select the correct saw blade for the material to
be cut.
3. Wear gloves when handling saw blades.
4. Clean the spindle, anges (especially the
installing surface) and hex nut before install-
ing the blade. Poor installation may cause vibra-
tion/wobbling or slippage of the blade.
5. Do not cut metal objects such as nails and
screws. Inspect for and remove all nails,
screws and other foreign material from the
workpiece before operation.
6. NEVER permit anyone else to stand in line with
the path of the saw blade.
7. Before using the tool on an actual workpiece,
let it run for a while. Watch for vibration or
wobbling that could indicate poor installation
or a poorly balanced blade.
8. The tool should not be used for slotting, rab-
betting or grooving.
9. Replace the table insert when worn.
10. Always store the push-stick when it is not in
use.
11. Knock out any loose knots from workpiece
BEFORE beginning to cut.
12. Some dust created from operation contains
chemicals known to cause cancer, birth
defects or other reproductive harm Some
examples of these chemicals are:
— lead from lead-based-painted material
and,
— arsenic and chromium from chemical-
ly-treated lumber.
Your risk from these exposures varies,
depending on how often you do this type
of work. To reduce your exposure to these
chemicals: work in a well ventilated area and
work with approved safety equipment, such as
those dust masks that are specially designed
to lter out microscopic particles.

12 ENGLISH
13. Always make sure that sub guard is down and
at against saw-table before plugging in the
tool.
14. Inspect extension cords periodically and
replace if damaged.
15. (For European countries only)
Use only saw blades recommended by the
manufacturer and which conform to EN847-1.
INSTALLATION
Positioning table saw
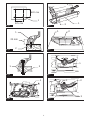
► Fig.1: 1. Hole diameter 8 mm
► Fig.2: 1. 6 mm Std. washer 2. No.10 wood screw 40
mm min. length
► Fig.3: 1. 6 mm Std. washer 2. 6 mm Mounting bolt
& Nut tighten securely
Locate the table saw in a well lit and level area where
you can maintain good footing and balance. It should
be installed in an area that leaves enough room to
easily handle the size of your workpieces. The table
saw should be secured with four screws or bolts to the
work bench or table saw stand using the holes provided
in the bottom of the table saw. When securing the table
saw on the work bench, make sure that there is an
opening in the top of the work bench the same size as
the opening in the bottom of the table saw so the saw-
dust can drop through.
If during operation there is any tendency for the table
saw to tip over, slide or move, the work bench or table
saw stand should be secured to the oor.
Storing accessories
► Fig.4: 1. Miter gauge
► Fig.5: 1. Rip fence 2. Push stick 3. Anti-kickback
pawls
The miter gauge, saw blade and wrenches can be
stored on the left side of the base. Also the rip fence,
push stick, and anti-kickback pawls can be stored at the
right side of the base.
FUNCTIONAL
DESCRIPTION
CAUTION: Always be sure that the tool is
switched off and unplugged before adjusting or
checking function on the tool.
Blade guard
WARNING: Never defeat or remove the blade
guard. An exposed blade as a result of defeated
guarding may result in serious personal injury during
operation.
WARNING: Never use the tool if the blade
guard is damaged, faulty or removed. Operation of
the tool with a damaged, faulty or removed guard may
result in serious personal injury.
► Fig.6: 1. Blade guard 2. Sub guard
When cutting, push the workpiece toward the blade
with the lower edge of the sub guard contacting with the
main table. As the workpiece is fed, the blade guard and
the sub guard goes over the edge of the workpiece.
In the interest of your personal safety, always maintain
the blade guard and sub guard in good condition. Any
irregular operation of the blade guard and sub guard
should be corrected immediately. Check to assure that
the blade guard and the sub guard are down and the
lower edge of the sub guard contacts with the main
table when the workpiece is not fed.
If the see-through parts become dirty, or sawdust
adheres to them in such a way that the blade and/or
workpiece is no longer easily visible, unplug the tool
and clean the see-through parts carefully with a damp
cloth. Do not use solvents or any petroleum-based
cleaners because this may cause damage to the parts.
If see-through parts become discolored through age or
UV light exposure, contact a Makita service center for
a new parts. DO NOT DEFEAT OR REMOVE BLADE
GUARD AND SUB GUARD.
Adjusting the depth of cut
► Fig.7: 1. Handle
The depth of cut may be adjusted by turning the handle.
Turn the handle clockwise to raise the saw blade or
counterclockwise to lower it.
NOTE: Use a shallow depth setting when cutting thin
materials in order to obtain a cleaner cut.
Adjusting the bevel angle
► Fig.8: 1. Lock lever 2. Arrow pointer 3. Handwheel
Loosen the lock lever counterclockwise and turn the
handwheel until the desired angle (0° - 45°) is obtained.
The bevel angle is indicated by the arrow pointer.
After obtaining the desired angle, tighten the lock lever
clockwise to secure the adjustment.
CAUTION: After adjusting the bevel angle, be
sure to tighten the lock lever securely.

13 ENGLISH
Adjusting positive stops
► Fig.9: 1. 90°Adjusting screw 2. 45°Adjusting screw
► Fig.10
The tool is equipped with positive stops at 90° and 45°
to the table surface. To check and adjust the positive
stops, proceed as follows:
Move the handwheel as far as possible by turning it.
Place a triangular rule on the table and check to see
if the saw blade is at 90° or 45° to the table surface. If
the saw blade is at an angle shown in Fig. A, turn the
adjusting screws clockwise; if it is at an angle shown in
Fig. B, turn the adjusting screws counterclockwise to
adjust the positive stops.
After adjusting the positive stops, set the saw blade at
90° to the table surface. Then adjust the arrow pointer
so that its right edge is aligned to the 0° graduation.
► Fig.11: 1. Arrow pointer
Switch action
► Fig.12: 1. Switch
CAUTION: Before operation, make sure that
the tool is turned on and off.
To start the tool, press the ON ( I ) button.
To stop it, press the OFF ( O ) button.
Sub fence (rip fence)
► Fig.13: 1. Clamping screw 2. Rip fence 3. Sub
fence 4. Rail
If the rip fence comes close to the saw blade, use the
sub fence to support the workpiece. Loosen the clamp-
ing screw and slide the sub fence out of the rail. Attach
the sub fence as illustrated and tighten the clamping
screws.
When the rip fence is attached to the left side of the
saw blade, switch the sub fence position. Remove the
clamping screws, sub fence, and rail from the rip fence.
Loosely attach the rail on the right side of the rip fence
using the removed clamping screws. After that, attach
the sub fence and tighten the clamping screws.
► Fig.14: 1. Rip fence 2. Sub fence 3. Clamping
screw 4. Rail
Sub table (R)
► Fig.15: 1. Lever
► Fig.16: 1. Sub table (R)
This tool is provided with the sub table (R) on the right
side of the main table. To use the sub table (R), raise
both levers on the front right side, pull out the table (R)
fully and then lower the levers to secure it.
When using the sub table (R ), locate the scale plate
on the sub table after loosening the screw on it with
a screwdriver so that it becomes successive with the
scale plate on the main table.
► Fig.17: 1. Scale plate 2. Screw
Sub table (back)
Optional accessory
► Fig.18: 1. Sub table (back) 2. Screw
To use the sub table (back), loosen the screws on the
left and right hand sides under the table and pull it out
backwards to the desired length. At the desired length,
tighten the screws securely.
NOTE:
When using the sub table (back) during use of the
rip fence, pull out the sub table (back) more than 50 mm
so that it does not hit against the top end of the rip fence.
Sub table (L)
Optional accessory
► Fig.19: 1. Screw 2. Sub table (L)
Sub table (L) (optional accessory) can be installed on
the left side of the table to obtain wider space.
Anti-kickback pawls
WARNING: Use the Antikickback pawls when-
ever possible during the through cutting opera-
tions. This will help prevent the material from being
pushed forward into the operator during a kickback
situation which may result in serious personal injury.
► Fig.20: 1. Antikickback pawl 2. Clamp
To remove the anti-kickback pawls from the tool, loosen the
clamp on the root of the antikickback pawls and then pull them
out. To install, perform the removal procedure in reverse.
ASSEMBLY
CAUTION: Always be sure that the tool is
switched off and unplugged before carrying out
any work on the tool.
Installing or removing saw blade
CAUTION: Always be sure that the tool is
switched off and unplugged before installing or
removing the saw blade.
CAUTION: Use only the Makita wrench pro-
vided to install or remove the saw blade. Failure
to do so may result in overtightening or insufcient
tightening of the hex bolt. This could cause an injury.
CAUTION: Use the following saw blade. Do
not use saw blades which do not comply with the
characteristics specied in these instructions.
Diameter Blade thickness Kerf
260 mm Less than 1.9 mm More than 2.1 mm
1.
Loosen the screw on the table insert and remove it.
2. Hold the outer ange with the offset wrench and
loosen the hex nut counterclockwise with the wrench.
Then remove the outer ange.
► Fig.21: 1. Offset wrench 2. Hex nut 3. Wrench

14 ENGLISH
3. Assemble the inner ange, ring, saw blade, outer
ange and hex nut onto the arbor, making sure that the
teeth of the blade are pointing down at the front of the
table. Always install the hex nut with its recessed side
facing the outer ange.
► Fig.22: 1. Inner ange 2. Ring 3. Saw blade
4. Outer ange 5. Hex nut
CAUTION: Be sure that the saw blade is
installed so that the teeth are aligned in the cut-
ting (turning) direction.
CAUTION: Check the arbor hole diameter of
the saw blade before installing the saw blade.
Always use the correct ring for the arbor hole of
the saw blade you intend to use. The size of the
supplied ring(s) varies depending on the country.
• For tool for a 30 mm hole-diameter saw blade,
the ring 30 mm in outer diameter is provided.
• For tool for a 25.4 mm and 25 mm hole-diameter
saw blade, the silver and black rings are pro-
vided. Use the silver ring for 25.4 mm hole-di-
ameter saw blade and the black ring for 25 mm
hole-diameter saw blade.
4. To secure the saw blade in place, hold the outer
ange with the offset wrench, then tighten the hex nut
clockwise with the wrench. BE SURE TO TIGHTEN
THE HEX NUT SECURELY.
► Fig.23: 1. Offset wrench 2. Wrench
CAUTION
: Keep the ange surface clean of dirt or
other adhering matter; it could cause blade slippage.
CAUTION: Be sure to hold the hex nut care-
fully with the wrench. If your grip should slip, the
wrench may come off the hex nut, and your hand
could strike the sharp blade edges.
5. Attach the table insert in place with the screw.
Adjusting the riving knife
CAUTION:
If the saw blade and riving knife are
not aligned properly, a dangerous pinching condi-
tion may result during operation. Make sure they are
properly aligned. You could suffer serious personal injury
while using the tool without a properly aligned riving knife.
CAUTION: NEVER make any adjustments
while tool is running. Disconnect the tool before
making any adjustments.
CAUTION: Don't remove the riving knife.
► Fig.24: 1. Blade guard 2. Riving knife 3. Screw
The riving knife position is factory-adjusted so that
the saw blade and riving knife will be in a straight line.
However, you need to adjust it if the saw blade and
riving knife are not in a straight line.
Loosen the screw on the table insert and remove it from the
main table. Loosen the hex bolts (B) and adjust the blade
guard mounting portion (stay) so that the riving knife is
aligned directly behind the saw blade. Then tighten the hex
bolts (B) to secure the stay and put the table insert in place.
► Fig.25: 1. Blade 2. These two clearances should be
equal. 3. Riving knife 4. Hex bolts (B) 5. Hex
bolts (A)
There must be a clearance of about 4 - 5 mm between
the riving knife and the blade teeth. Loosen the hex
bolts (A), adjust the riving knife accordingly and tighten
the hex bolts (A) securely. Attach the table insert on the
table with the screw, then check to see that the blade
guard works smoothly before cutting.
► Fig.26: 1. Riving knife 2. Blade guard 3. 4 mm -
5mm clearance
Installing and adjusting rip fence
► Fig.27: 1. Hook 2. Knob 3. Guide rail
1. Fit the hook on the tip of the rip fence into the far
guide rail on the table or sub table (R) and install and
push the rip fence forward so that the fence holder
engages with the nearmost guide rail.
2. To slide the rip fence on the guide rail sideways,
return the knob on the fence holder fully without pulling
the lever on the knob.
To secure the rip fence, pivot fully the knob on the fence
holder.
3. To remove the rip fence, pull the lever on the knob
and pivot the knob fully forward while pulling the lever.
To check if the rip fence is parallel with the saw blade,
secure the rip fence 2 - 3 mm from the saw blade. Raise
the blade up to maximum elevation. Mark one of the
blade teeth with a crayon. Measure the distance (A)
and (B) between the rip fence and saw blade. Take both
measurements using the tooth marked with the crayon.
These two measurements should be identical. If the
rip fence is not parallel with the saw blade, proceed as
follows:
► Fig.28: 1. Scale
1. Position the rip fence in the sliding position.
2. Loosen the two hex bolts on the rip fence with the
hex wrench provided.
► Fig.29: 1. Hex bolts
3. Adjust the rip fence until it becomes parallel with
the saw blade.
4.
Pivot down the knob on the rip fence toward the operator.
5. Tighten the two hex bolts on the rip fence.
► Fig.30
CAUTION: Be sure to adjust the rip fence so
that it is parallel with the saw blade, or a danger-
ous kickback condition may occur.
When the rip fence cannot be secured solidly, adjust it
according to the following procedure.
1. Set the rip fence on the table and then pivot the
knob on the half way of its travel (moving position).
Tighten the screw (A) until the rip fence is immobilized.
Then loosen a 1/4 to 1/2 turn.
► Fig.31: 1. Rip fence 2. Released position 3. Moving
position 4. Lock position
► Fig.32: 1. Rip fence 2. Moving position 3. Screw (B)
4. Screw (A)
2. Tighten the screw (B) fully and then loosen about
2 full revolutions.
3. Lock the rip fence by fully pivoting the knob on the
fence holder (lock position).

15 ENGLISH
4. Make sure that the rip fence can be installed and
removed in the original position (released position).
5. Make sure that the rip fence can be slid smoothly
with no wobble when the knob is on half way of its
travel.
NOTICE: Be careful not to tighten screws with
more than tightening amount specied in the
above instructions. Failure to do so may damage
the fastened parts.
Bring the rip fence up ush against the side of the saw
blade. Make sure that the guideline on the fence holder
points to the 0 graduation. If the guideline does not
point to the 0 graduation, loosen the screw on the scale
plate and adjust the scale plate.
► Fig.33: 1. Guideline 2. Screws
Connecting to vacuum cleaner
Cleaner operations can be performed by connecting the
tool to Makita vacuum cleaner or dust collector.
► Fig.34
OPERATION
CAUTION: Always use "work helpers" such
as push sticks and push blocks when there is a
danger that your hands or ngers will come close
to the saw blade.
CAUTION: Always hold the workpiece rmly
with the table and the rip fence or miter gauge. Do
not bend or twist it while feeding. If the workpiece
is bent or twisted, dangerous kickbacks may occur.
CAUTION: NEVER withdraw the workpiece
while the saw blade is running. If you must with-
draw the workpiece before completing a cut, rst
switch the tool off while holding the workpiece
rmly. Wait until the saw blade has come to a
complete stop before withdrawing the workpiece.
Failure to do so may cause dangerous kickbacks.
CAUTION: NEVER remove cut-off material
while the saw blade is running.
CAUTION: NEVER place your hands or n-
gers in the path of the saw blade. Be especially
careful with bevel cuts.
CAUTION: Always secure the rip fence rmly,
or dangerous kickbacks may occur.
CAUTION: Always use "work helpers" such
as push sticks and push blocks when cutting
small or narrow workpieces.
Work helpers
Push sticks, push blocks or auxiliary fence are types of
"work helpers". Use them to make safe, sure cuts with-
out the need for the operator to contact the saw blade
with any part of the body.
Push block
► Fig.35: 1. Face/edge parallel 2. Handle 3. Wood
screw 4. Glue together
Use a 19 mm piece of plywood.
Handle should be in center of plywood piece. Fasten
with glue and wood screws as shown. Small piece 9.5
mm x 8 mm x 50 mm of wood must always be glued to
plywood to keep the saw blade from dulling if the oper-
ator cuts into push block by mistake. (Never use nails in
push block.)
Auxiliary fence
► Fig.36: 1. Face/edge parallel
Make auxiliary fence from 9.5 mm and 19 mm plywood
pieces.
Ripping
CAUTION: When ripping, remove the miter
gauge from the table.
CAUTION: When cutting long or large work-
pieces, always provide adequate support behind
the table. DO NOT allow a long board to move
or shift on the table. This will cause the saw blade
to bind and increase the possibility of kickback and
personal injury. The support should be at the same
height as the table.
CAUTION: Do not perform bevel ripping on
the bevelling side of the saw blade.
1. Adjust the depth of cut a bit higher than the thick-
ness of the workpiece.
► Fig.37
2. Position the rip fence to the desired width of rip
and lock in place by pivoting the knob. Before ripping,
make sure the rear end of the rip fence is secured
rmly. If it is not secured enough, follow the procedures
in the section titled "Installing and adjusting rip fence".
3. Turn the tool on and gently feed the workpiece into
the saw blade along with the rip fence.
When the width of rip is 150 mm and wider, carefully
use your right hand to feed the workpiece. Use your left
hand to hold the workpiece in position against the rip
fence.
► Fig.38
When the width of rip is 65 mm - 150 mm wide, use the
push stick to feed the workpiece.
► Fig.39: 1. Push stick
When the width of rip is narrower than 65 mm, the push
stick cannot be used because the push stick will strike
the blade guard. Use the auxiliary fence and push
block. Attach the auxiliary fence to the rip fence with two
"C" clamps.
Feed the workpiece by hand until the end is about 25
mm from the front edge of the table.
► Fig.40
Continue to feed using the push block on the top of the
auxiliary fence until the cut is complete.
► Fig.41: 1. Push block 2. Auxiliary fence

16 ENGLISH
Cross cutting
CAUTION: When making a crosscut, remove
the rip fence from the table.
CAUTION: When cutting long or large work-
pieces, always provide adequate support to the
sides of the table. The support should be at the
same height as the table.
CAUTION: Always keep hands away from
path of blade.
Miter gauge
► Fig.42: 1. Cross cutting 2. Mitering 3. Bevel cutting
4. Compound mitering (angles)
Use the miter gauge for the 4 types of cutting shown in
the gure.
CAUTION: Secure the knob on the miter
gauge carefully.
CAUTION: Avoid creep of workpiece and
gauge by rm workholding arrangement, espe-
cially when cutting at an angle.
CAUTION: NEVER hold or grasp the intended
"cut-off" portion of the workpiece.
CAUTION: Always adjust the distance
between the end of the miter gauge and the saw
blade not to exceed 15 mm.
Miter gauge positive stop
► Fig.43: 1. Screw for positive stop 2. Small plate
3. Knob
Miter gauge is provided with positive stops at 90°,
45°right and left miter angles for quick setting of miter
angles.
To set the miter angle, loosen the knob on the miter
gauge.
Raise the small plate on the miter gauge for free setting.
Turn the miter gauge to the desired miter angle. Return
the small plate on the miter gauge to the original posi-
tion and tighten the knob clockwise securely.
Use of miter gauge
► Fig.44: 1. Groove 2. Miter gauge 3. Knob
Slide the miter gauge into the thick grooves in the table.
Loosen the knob on the gauge and align to desired
angle (0° to 60°). Bring stock ush up against fence and
feed gently forward into the saw blade.
Sub gauge (miter gauge)
► Fig.45: 1. Sub gauge
The sub gauge on the miter gauge prevents the work-
piece from wobbling. Loosen the screw on the miter
gauge and adjust the sub gauge position.
Carrying tool
► Fig.46
Make sure that the tool is unplugged.
Carry the tool by holding the tool part shown in the
gure.
CAUTION: Always secure all moving portions
before carrying the tool.
CAUTION: Before the carrying the tool, make
sure that the blade guard and the sub guard are
down and the lower edge of the sub guard con-
tacts with the main table.
MAINTENANCE
CAUTION: Always be sure that the tool is
switched off and unplugged before attempting to
perform inspection or maintenance.
NOTICE: Never use gasoline, benzine, thinner,
alcohol or the like. Discoloration, deformation or
cracks may result.
Cleaning
Clean out sawdust and chips from time to time. Carefully
clean the blade guard and moving parts inside the table saw.
When removing the sawdust accumulated under the
saw blade, remove the table insert and use an air
duster to blow out the sawdust from the connector for a
vacuum cleaner.
Lubrication
To keep the table saw in tip-top running condition, and
to assure maximum service life, oil or grease the mov-
ing parts and rotating parts from time to time.
Lubrication places:
• Threaded shaft to elevate the saw blade
• Hinge to rotate the frame
• Elevation guide shafts on motor
• Gear to elevate the saw blade
• Guide rails for the rip fence
• Shaft of the sub table (R) locking levers
• Sliding part of the sub table (R)
Replacing carbon brushes
Check the carbon brushes regularly.
Replace them when they wear down to the limit mark.
Keep the carbon brushes clean and free to slip in the
holders. Both carbon brushes should be replaced at the
same time. Use only identical carbon brushes.
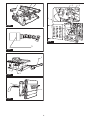
► Fig.47: 1. Limit mark
1. Store the sub table (R). Remove the rip fence if it
is stored.
2. Loosen the lock lever and turn the handwheel
until the saw head is tilted to 45° bevel angle. After that,
tighten the lock lever.
► Fig.48: 1. Rip fence 2. Lock lever 3. Handwheel

17 ENGLISH
3. Stand the tool on its right side.
► Fig.49
4. Loosen the screws on the bottom plate and
remove it.
5. Loosen the brush holder caps using a screwdriver
and remove the worn carbon brushes.
► Fig.50: 1. Bottom plate 2. Brush holder cap
3. Screwdriver
6. Insert the new carbon brushes and secure the
brush holder caps.
7. Attach the bottom plate with screws and carefully
lay the tool on its bottom. Store the rip fence if removed.
To maintain product SAFETY and RELIABILITY,
repairs, any other maintenance or adjustment should
be performed by Makita Authorized or Factory Service
Centers, always using Makita replacement parts.
OPTIONAL
ACCESSORIES
CAUTION: These accessories or attachments
are recommended for use with your Makita tool
specied in this manual. The use of any other
accessories or attachments might present a risk of
injury to persons. Only use accessory or attachment
for its stated purpose.
If you need any assistance for more details regard-
ing these accessories, ask your local Makita Service
Center.
• Steel & Carbide-tipped saw blades
• Sub table (L)
• Sub table (back)
• Rip fence
• Miter gauge
• Offset wrench 13-22
• Wrench 19
• Hex wrench 5
• Joint (for connecting to dust collector)
• Table stand set
Refer to the instruction manual for table saw stand
that is provided with the table saw stand as an optional
accessory.
NOTE: Some items in the list may be included in the
tool package as standard accessories. They may
differ from country to country.

18 POLSKI
POLSKI (Instrukcja oryginalna)
DANE TECHNICZNE
Model: 2704N
Otwór na trzpień
(w zależności od kraju) 30 mm/25,4 mm
Średnica tarczy 260 mm
Maks. zakres cięcia w pionie pod kątem 0° 93 mm
w pionie pod kątem 45° 64 mm
Prędkość bez obciążenia 5 200 min-1
Wielkość stołu (dług. x szer.)
ze stołami dodatkowymi (P) i (tył)
1 045 mm x 1 066 mm (stoły rozłożone)
665 mm x 753 mm (stoły złożone)
ze stołem dodatkowym (P)
bez stołu dodatkowego (tył) 567 mm x 1 066 mm (stół rozłożony)
567 mm x 753 mm (stół złożony)
Wymiary (dług. x szer. x wys.)
ze stołami złożonymi
ze stołami dodatkowymi (P) i (tył)
715 mm x 753 mm x 483mm
ze stołem dodatkowym (P)
bez stołu dodatkowego (tył) 665 mm × 753 mm × 483 mm
Masa netto 35,2–37,0 kg
Klasa bezpieczeństwa /II
• W związku ze stale prowadzonym przez naszą rmę programem badawczo-rozwojowym niniejsze dane mogą
ulec zmianom bez wcześniejszego powiadomienia.
• Dane techniczne mogą różnić się w zależności od kraju.
• Wysokość może być różna w zależności od osprzętu. W tabeli została przedstawiona najlżejsza i najcięższa
konguracja zgodnie z procedurą EPTA 01/2014.
Symbole
Poniżej pokazano symbole zastosowane na urządze-
niu. Przed rozpoczęciem użytkowania należy zapoznać
się z ich znaczeniem.
Przeczytać instrukcję obsługi.
PODWÓJNA IZOLACJA
Nosić okulary ochronne.
Dłonie i palce należy trzymać z dala od
tarczy.
Dotyczy tylko państw UE
Nie wyrzucać urządzeń elektrycznych wraz
z odpadami z gospodarstwa domowego!
Zgodnie z dyrektywą europejską w sprawie
zużytego sprzętu elektrycznego i elektro-
nicznego oraz dostosowaniem jej do prawa
krajowego, zużyte urządzenia elektryczne
należy składować osobno i przekazywać
do zakładu recyklingu działającego zgod-
nie z przepisami dotyczącymi ochrony
środowiska.
Przeznaczenie
To narzędzie jest przeznaczone do cięcia w drewnie.
Za pomocą tego narzędzia można wykonywać cięcie
proste, cięcie pod kątem w pionie i cięcie pod kątem w
poziomie. Narzędzie to nie jest przeznaczone do cięcia
nieprzelotowego.
Zasilanie
Narzędzie wolno podłączać tylko do źródeł zasilania o
napięciu zgodnym z napięciem podanym na tabliczce
znamionowej. Można je zasilać wyłącznie jednofazo-
wym prądem przemiennym. Narzędzie ma podwójną
izolację, dlatego też można je zasilać z gniazda elek-
trycznego bez uziemienia.
Hałas
Typowy równoważny poziom dźwięku A określony w
oparciu o normę EN62841:
Poziom ciśnienia akustycznego (LpA): 94 dB(A)
Poziom mocy akustycznej (LWA): 107 dB (A)
Niepewność (K): 3 dB(A)
OSTRZEŻENIE: Nosić ochronniki słuchu.
Deklaracja zgodności WE
Dotyczy tylko krajów europejskich
Deklaracja zgodności WE jest dołączona jako załącznik
A do niniejszej instrukcji obsługi.

19 POLSKI
OSTRZEŻENIA
DOTYCZĄCE
BEZPIECZEŃSTWA
Ogólne zasady bezpiecznej
eksploatacji elektronarzędzi
OSTRZEŻENIE: Należy zapoznać się z
ostrzeżeniami dotyczącymi bezpieczeństwa,
instrukcjami, ilustracjami i danymi technicz-
nymi dołączonymi do tego elektronarzędzia.
Niezastosowanie się do podanych poniżej instrukcji
może prowadzić do porażenia prądem, pożaru i/lub
poważnych obrażeń ciała.
Wszystkie ostrzeżenia i instruk-
cje należy zachować do wykorzy-
stania w przyszłości.
Pojęcie „elektronarzędzie", występujące w wymienio-
nych tu ostrzeżeniach, odnosi się do elektronarzędzia
zasilanego z sieci elektrycznej (z przewodem zasilają-
cym) lub do elektronarzędzia akumulatorowego (bez
przewodu zasilającego).
Instrukcje bezpieczeństwa dotyczące
stołowych pilarek tarczowych
Ostrzeżenia związane z osłonami
1. Osłony powinny być założone. Osłony muszą
być sprawne i muszą być prawidłowo zamon-
towane. Jeśli osłona jest luźna, została uszko-
dzona lub nie działa prawidłowo, należy ją napra-
wić lub wymienić.
2.
Przed włączeniem narzędzia za pomocą przełącz-
nika należy się upewnić, że tarcza tnąca nie dotyka
osłony, klina rozszczepiającego lub obrabianego
elementu. Przypadkowe zetknięcie tych elementów z
tarczą tnącą może spowodować zagrożenie.
3.
Należy wyregulować klin rozszczepiający w sposób
opisany w niniejszej instrukcji obsługi. Niepoprawne
ustawienie, zła pozycja i złe dopasowanie mogą
powodować nieskuteczność klina rozszczepiającego w
zmniejszeniu prawdopodobieństwa odrzutu.
4.
Aby klin rozszczepiający i zapadki zapobiega-
jące odrzutowi działały poprawnie, muszą być
połączone w obrabianym elemencie. Klin rozsz-
czepiający i zapadki zapobiegające odrzutowi nie
będą działać prawidłowo podczas cięcia obrabianych
elementów, które są zbyt krótkie, aby możliwe było
ich połączenie z klinem lub zapadkami. W takich
warunkach klin rozszczepiający i zapadki zapobiega-
jące odrzutowi nie będą przeciwdziałać odrzutowi.
5. Należy używać właściwej tarczy tnącej do klina
rozszczepiającego. Aby klin rozszczepiający
działał prawidłowo, średnica tarczy tnącej musi
być dopasowana do klina rozszczepiającego,
tarcza tnąca musi być cieńsza niż grubość
klina rozszczepiającego, a szerokość cięcia
tarczy tnącej musi być szersza od grubości klina
rozszczepiającego.
Ostrzeżenia dotyczące procedur cięcia
1. NIEBEZPIECZEŃSTWO: Nigdy nie należy
zbliżać palców ani dłoni do tarczy tnącej.
Chwila nieuwagi lub poślizgnięcie się może spra-
wić, że dłoń zbliży się do tarczy tnącej i dojdzie do
poważnych obrażeń ciała.
2. Obrabiany element należy przesuwać w stronę
tarczy tnącej tylko przeciwnie do kierunku
obrotów. Przesuwanie obrabianego elementu
zgodnie z kierunkiem obrotów tarczy tnącej nad
stołem może spowodować wciągnięcie obrabia-
nego elementu i dłoni przez tarczę tnącą.
3. Nigdy nie należy używać przyrządu do ukoso-
wania do przesuwania obrabianego elementu
podczas cięcia wzdłużnego, a prowadnicy
wzdłużnej jako ogranicznika długości podczas
cięcia poprzecznego z użyciem przyrządu do
ukosowania. Prowadzenie obrabianego elementu
za pomocą prowadnicy wzdłużnej i przyrządu do
ukosowania jednocześnie zwiększa prawdopodo-
bieństwo zablokowania tarczy tnącej i odrzutu.
4.
Podczas cięcia wzdłużnego siłę do przesuwania
obrabianego detalu należy przyłożyć pomiędzy
prowadnicą a tarczą tnącą. Jeśli odległość pomię-
dzy prowadnicą a tarczą tnącą jest mniejsza
niż 150 mm, należy użyć popychacza, a jeśli ta
odległość jest mniejsza niż 50 mm, należy użyć
dociskacza. Dzięki „narzędziom pomocniczym” dłoń
pozostanie w bezpiecznej odległości od tarczy tnącej.
5.
Należy używać wyłącznie popychacza dostarczo-
nego przez producenta lub wyprodukowanego
zgodnie z instrukcjami. Dzięki popychaczowi dłoń
znajduje się w odpowiedniej odległości od tarczy tnącej.
6.
Nigdy nie należy używać uszkodzonego lub nacię-
tego popychacza. Uszkodzony popychacz może się
złamać, powodując ześlizgnięcie dłoni na tarczę tnącą.
7.
Nie należy wykonywać żadnych operacji
„odręcznie”. Do ustawienia i poprowadzenia
obrabianego elementu zawsze należy używać
prowadnicy wzdłużnej lub przyrządu do ukoso-
wania. „Odręcznie” oznacza podtrzymywanie lub
prowadzenie obrabianego elementu rękami a nie
przy użyciu prowadnicy wzdłużnej lub przyrządu
do ukosowania. Odręczne cięcie prowadzi do nie-
prawidłowego ustawienia, zablokowania i odrzutu.
8. Nigdy nie należy sięgać ręką w pobliżu lub
nad obracającą się tarczą tnącą. Sięgnięcie do
obrabianego elementu może spowodować przy-
padkowy kontakt z poruszającą się tarczą tnącą.
9. W przypadku długich i/lub szerokich obrabia-
nych elementów należy zapewnić pomocnicze
podparcie elementu z tyłu i/lub po bokach
stołowej pilarki tarczowej, które pozwoli
utrzymać je w poziomie. Długie i/lub szerokie
elementy obrabiane mają tendencję do obracania
się na krawędzi stołu, co powoduje utratę kontroli,
zablokowanie tarczy tnącej i odrzut.
10. Obrabiany element należy przesuwać w
równym tempie. Nie należy zginać ani obra-
cać obrabianego elementu. W przypadku
zakleszczenia należy niezwłocznie wyłączyć
narzędzie, odłączyć je od zasilania i usunąć
przyczynę zakleszczenia. Zakleszczenie tarczy
tnącej przez obrabiany element może spowodo-
wać odrzut lub zgaśnięcie silnika.

20 POLSKI
11. Nie należy wyjmować fragmentów ciętego
materiału w czasie pracy pilarki. Materiał może
utknąć pomiędzy prowadnicą lub pomiędzy osłoną
tarczy tnącej i tarczą, co spowoduje wciągnięcie
palców przez tarczę tnącą. Przed usunięciem
materiału należy wyłączyć pilarkę i poczekać, aż
tarcza tnąca zatrzyma się.
12.
Podczas cięcia wzdłużnego elementów o grubo-
ści mniejszej niż 2 mm należy użyć prowadnicy
pomocniczej, która styka się z powierzchnią
stołu. Cienki element obrabiany może zaklinować
się pod prowadnicą wzdłużną i spowodować odrzut.
Przyczyny odrzutu i związane z tym ostrzeżenia
Odrzut to nagła reakcja obrabianego elementu spowo-
dowana przez ściśnięcie, zakleszczenie tarczy tnącej
lub niewłaściwą linię cięcia obrabianego elementu w
odniesieniu do tarczy tnącej lub reakcja na zaklesz-
czenie obrabianego elementu pomiędzy tarczą tnącą i
prowadnicą wzdłużną lub innym stałym obiektem.
Najczęściej podczas odrzutu obrabiany element zostaje
uniesiony nad stołem w tylnej części tarczy tnącej i
wyrzucony w kierunku operatora.
Odrzut jest wynikiem nieprawidłowego używania pilarki
i/lub niewłaściwych procedur lub warunków jej obsługi.
Można tego uniknąć, podejmując odpowiednie środki
ostrożności, które podano poniżej.
1.
Nigdy nie należy stawać bezpośrednio w jednej
linii z tarczą tnącą. Zawsze należy stawać po
tej samej stronie tarczy tnącej, co prowadnica
wzdłużna. Odrzut może spowodować wyrzucenie
obrabianego elementu z dużą prędkością w kierunku
osoby stojącej z przodu i w jednej linii z tarczą tnącą.
2.
W celu pociągnięcia lub podparcia obrabianego
elementu nigdy nie należy sięgać nad tarczą
tnącą ani za nią. Może wówczas dojść do przy-
padkowego kontaktu z tarczą tnącą lub wciągnięcia
palców przez tarczę tnącą w wyniku odrzutu.
3. Nigdy nie należy przytrzymywać ani dociskać
obrabianego elementu, który jest cięty przez
obracającą się tarczę tnącą. Dociśnięcie obra-
bianego elementu w trakcie cięcia do tarczy tnącej
spowoduje zakleszczenie i odrzut.
4. Osłonę należy ustawić równolegle do tarczy
tnącej. Źle ustawiona osłona przyciśnie obrabiany
element do tarczy tnącej i spowoduje odrzut.
5.
Należy zachować szczególną ostrożność podczas
wykonywana cięcia w zasłoniętych przestrze-
niach zamontowanych obrabianych elementów.
Wystająca tarcza tnąca może przeciąć niewidoczne
elementy, co z kolei może wywołać odrzut.
6. Duże płyty należy podpierać, aby zminimali-
zować ryzyko zakleszczania się tarczy tnącej
i odrzutu. Duże płyty mają tendencję do wygina-
nia się pod własnym ciężarem. Podpory należy
umieszczać pod wszystkimi częściami płyty
wystającymi poza powierzchnię stołu.
7. Należy zachować szczególną ostrożność pod-
czas cięcia obrabianego elementu, który jest
skręcony, ma sęki, jest zniekształcony lub nie
ma prostej krawędzi umożliwiającej prowadze-
nie go za pomocą przyrządu do ukosowania
lub wzdłuż prowadnicy. Obrabiany element,
który jest zniekształcony, skręcony lub ma sęki,
jest niestabilny i może spowodować niewłaściwe
ustawienie nacięcia w odniesieniu do tarczy tną-
cej, zakleszczenie i odrzut.
8. Nigdy nie należy ciąć kilku elementów uło-
żonych na sobie pionowo lub poziomo. Pod
tarczę tnącą może dostać się jeden lub kilka ele-
mentów i może dojść do odrzutu.
9. Przed ponownym uruchomieniem pilarki z
tarczą tnącą znajdującą się w obrabianym
elemencie należy ustawić tarczę tnącą w
środku nacięcia tak, aby zęby tarczy nie były
wbite w materiał. Jeśli tarcza tnąca zablokuje
się, po ponownym uruchomieniu pilarki może ona
wypchnąć obrabiany element ku górze i doprowa-
dzić do wystąpienia odrzutu.
10. Tarcze tnące należy utrzymywać w czystości,
powinny być ostre i odpowiednio rozmiesz-
czone. Nigdy nie należy używać odkształco-
nych tarcz tnących ani tarcz z popękanymi lub
złamanymi zębami. Naostrzone i prawidłowo
ustawione tarcze tnące minimalizują ryzyko zak-
leszczenia, odrzutu i zgaśnięcia silnika.
Ostrzeżenia związane z procedurą obsługi stołowej
pilarki tarczowej
1. Podczas wyjmowania wkładki stołu, zmiany
tarczy tnącej lub ustawiania klina rozszczepia-
jącego, zapadek zapobiegających odrzutowi
lub osłony tarczy tnącej oraz w przypadku
pozostawienia maszyny bez nadzoru należy
wyłączyć stołową pilarkę tarczową i odłączyć
przewód zasilający. Środki zapobiegawcze
pozwolą uniknąć wypadków.
2.
Nigdy nie należy pozostawiać włączonej stołowej
pilarki tarczowej bez nadzoru. Należy ją wyłączyć
i nie zostawiać narzędzia przed jego całkowitym
zatrzymaniem. Pozostawiona bez nadzoru działająca
pilarka stanowi niekontrolowane zagrożenie.
3. Stołową pilarkę tarczową należy ustawić w
dobrze oświetlonym miejscu i na płaskiej
powierzchni zapewniającej dobre podparcie i
utrzymanie równowagi. Należy ją zamontować
w miejscu zapewniającym swobodną obsługę
obrabianych elementów o wybranej wielkości.
Ciemne, ciasne miejsca i nierówna, śliska podłoga
zwiększają ryzyko wypadków.
4. Należy często sprzątać i usuwać trociny
znajdujące pod stołową pilarką tarczową i/lub
pochłaniaczem pyłu. Nagromadzone trociny są
palne i może dojść do ich samozapłonu.
5. Stołową pilarkę tarczową należy przymoco-
wać. Jeśli stołowa pilarka tarczowa nie zostanie
przymocowana, może się poruszyć lub wywrócić.
6. Przed włączeniem stołowej pilarki tarczowej
należy usunąć ze stołu narzędzia, kawałki
drewna itp. Roztargnienie lub potencjalne zak-
leszczenie może być niebezpieczne.
7.
Zawsze należy używać tarcz tnących o prawidło-
wym rozmiarze i kształcie (romb lub koło) otwo-
rów na trzpień. Tarcze tnące, które nie pasują do
osprzętu do ich montażu w narzędziu, będą obracać
się mimośrodowo, powodując utratę kontroli.
8. Nigdy nie należy używać uszkodzonych lub
niewłaściwych elementów mocujących tarczy
tnącej, takich jak kołnierze, podkładki tarczy
tnącej, śruby lub nakrętki. Te elementy mocu-
jące zostały specjalnie zaprojektowane dla danej
pilarki, tak aby zapewniały bezpieczną pracę i
optymalną wydajność.
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
Pagina se încarcă...
-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
-
 29
29
-
 30
30
-
 31
31
-
 32
32
-
 33
33
-
 34
34
-
 35
35
-
 36
36
-
 37
37
-
 38
38
-
 39
39
-
 40
40
-
 41
41
-
 42
42
-
 43
43
-
 44
44
-
 45
45
-
 46
46
-
 47
47
-
 48
48
-
 49
49
-
 50
50
-
 51
51
-
 52
52
-
 53
53
-
 54
54
-
 55
55
-
 56
56
-
 57
57
-
 58
58
-
 59
59
-
 60
60
-
 61
61
-
 62
62
-
 63
63
-
 64
64
-
 65
65
-
 66
66
-
 67
67
-
 68
68
-
 69
69
-
 70
70
-
 71
71
-
 72
72
-
 73
73
-
 74
74
-
 75
75
-
 76
76
-
 77
77
-
 78
78
-
 79
79
-
 80
80
-
 81
81
-
 82
82
-
 83
83
-
 84
84
în alte limbi
- slovenčina: Makita 2704N Používateľská príručka
- polski: Makita 2704N Instrukcja obsługi
- Deutsch: Makita 2704N Benutzerhandbuch
Lucrări înrudite
-
Makita LF1000 Manual de utilizare
-
Makita LH1040 Manual de utilizare
-
Makita 5704R Manual de utilizare
-
Makita 5017RKB Manual de utilizare
-
Makita 5903R Manual de utilizare
-
Makita LS003GZ01 Manual de utilizare
-
home makita Manual de utilizare
-
Makita SP6000 Manual de utilizare
-
Makita 5104 Manual de utilizare
-
Makita MT582 Manualul proprietarului
Alte documente
-
Ryobi RPLS18X Manual de utilizare
-
Hikoki C 6U3 Circular Saw Manual de utilizare
-
Bosch GTS 635-216 Manual de utilizare
-
 Raider Power Tools RD-TS20 Manual de utilizare
Raider Power Tools RD-TS20 Manual de utilizare
-
BorMann BDX2150 Manual de utilizare
-
Bosch GTS 10 XC Manual de utilizare
-
Bosch GTS 10 XC Manual de utilizare
-
 Wellis ASPERO WB00392 Manual de utilizare
Wellis ASPERO WB00392 Manual de utilizare





















































































