Yamaha DS2416 Manualul proprietarului
- Categorie
- Mixere audio
- Tip
- Manualul proprietarului

COMPLIANCE INFORMATION STATEMENT
(DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY PROCEDURE)
Responsible Party: YAMAHA CORPORATION OF AMERICA
Address: 6600 Orangethorpe Avenue, Buena Park, Calif. 90620 U.S.A.
Telephone: 1-714-522-9011
FAX: 1-714-739-2680
Type of Equipment: DIGITAL MIXING CARD
Model Name: DS2416
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
Operation is subject to the following conditions:
1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and
2) this device must accept any interference received including interference that may cause undesired operation.
FCC INFORMATION (U.S.A.)
1. IMPORTANT NOTICE: DO NOT MODIFY THIS UNIT! This product, when installed as indicated in the instructions contained in this manual, meets FCC
requirements. Modifications not expressly approved by Yamaha may void your authority, granted by the FCC, to use the product.
2. IMPORTANT: When connecting this product to accessories and/or another product use only high quality shielded cables. Cable/s supplied with this product MUST
be used. Follow all installation instructions. Failure to follow instructions could void your FCC authorization to use this product in the USA.
3. NOTE: This product has been tested and found to comply with the requirements listed in FCC Regulations, Part 15 for Class “B” digital devices. Compliance with
these requirements provides a reasonable level of assurance that your use of this product in a residential environment will not result in harmful interference with
other electronic devices. This equipment generates/uses radio frequencies and, if not installed and used according to the instructions found in the users manual, may
cause interference harmful to the operation of other electronic devices. Compliance with FCC regulations does not guarantee that interference will not occur in all
installations. If this product is found to be the source of interference, which can be determined by turning the unit “OFF” and “ON”, please try to eliminate the
problem by using one of the following measures: Relocate either this product or the device that is being affected by the interference. Utilize power outlets that are on
different branch (circuit breaker or fuse) circuits or install AC line filter/s. In the case of radio or TV interference, relocate/reorient the antenna. If the antenna lead-in
is 300 ohm ribbon lead, change the lead-in to coaxial type cable. If these corrective measures do not produce satisfactory results, please contact the local retailer
authorized to distribute this type of product. If you can not locate the appropriate retailer, please contact Yamaha Corporation of America, Electronic Service
Division, 6600 Orangethorpe Ave, Buena Park, CA 90620
The above statements apply ONLY to those products distributed by Yamaha Corporation of America or its subsidiaries.

1
DS2416—Owner’s Manual
Contents
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Yamaha DSP Factory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Important Note . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
System Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
System Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Compatible Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Mixer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Recorder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Rear . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Internal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Installing the DS2416 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Testing the DS2416 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Installing the Test Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Using the Test Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Wordclocks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Recording Digitally to the DS2416 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Recording Digitally to DAT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Digitally Cascading DS2416 Cards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
DS2416 Q&A (Questions & Answers) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Effects Programs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Effects Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149

2
DS2416—Owner’s Manual
Important Notices
• Do not place the DS2416 in an area subject to excessive heat, direct sun-
light, excessive humidity, or dust.
• Keep the DS2416 inside its antistatic bag until you are ready to install it.
• To prevent handling damage, hold the DS2416 by the edges or bracket.
• If you accidentally touch the card edge connections, remove any finger-
prints using a dry tissue.
• Do not place objects on top of the DS2416, and do not put it down in a
place where other objects are likely to be placed on top of it.
• Before removing your computer’s cover, turn it off and remove the power
cord.
• To prevent static electricity damage, touch a grounded metal part of your
computer, such as the power supply case, before handling the DS2416.
Packing List
• DS2416 Digital Mixing Card
• Driver and Test program floppy disk
• 14-pin to 16-pin cable
• This manual
Trademarks
IBM PC is a registered trademark of International Business Machines. Korg is
a trademark of Korg, Inc. Pentium is a registered trademark of Intel. Sound
Blaster is a registered trademark of Advanced WavEffects. Windows 95 is a
trademark of Microsoft. Yamaha is a trademark of Yamaha Corporation. All
other trademarks are the property of their respective holders and are hereby
acknowledged.
Copyright
No part of the DS2416
Owner’s Manual
may be reproduced or distributed in
any form or by any means without the prior written authorization of Yamaha
Corporation, Inc.
© 1998 Yamaha Corporation. All rights reserved.
Keep this manual for future reference!

Introduction
3
DS2416—Owner’s Manual
Introduction
Thank you for purchasing the Yamaha DS2416 Digital Mixing Card. With
8-track simultaneous recording, 16-track simultaneous playback, 24-channel
mixing, 4-band parametric EQ, effects, and dynamics, the DS2416 provides a
complete digital recording studio inside a regular personal computer. Unlike
other audio cards, the DS2416’s five DSPs take the load off the computer’s
main processor leaving it free to concentrate on timing and other tasks while
the DS2416 takes care of high-quality effects, EQ, and dynamics processing.
In some cases, the DS2416’s onboard processing powerhouse may allow audio
software to record and playback a greater number of tracks.
For ease of installation and high data throughput, the DS2416 uses the indus-
try-standard PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) bus. Sound cards can
be connected digitally, or two DS2416 cards can be digitally cascaded for
48-channel mixing, each providing 2-channel analog inputs and outputs,
with 20-bit 128-times oversampling A/D converters and 20-bit 8-times over-
sampling D/A converters, and stereo coaxial digital input and output. Inputs
and outputs can be expanded using the optional AX44 Audio Expansion Unit,
which offers four 1/4-inch analog inputs—two of which can be used with
microphones—four 1/4-inch analog outputs and a stereo headphone jack.
Two AX44s can be used with each DS2416 card for eight analog inputs and
outputs.
Yamaha DSP Factory
The DS2416 Digital Mixing Card forms the heart of the Yamaha DSP Factory
system, a range of products designed to bring professional digital multitrack
recording and mixing to personal computers. Other DSP Factory products
include the AX44 Audio Expansion Unit, and several analog and digital
multi-channel input and output options are currently under development.
Check out the Yamaha Professional Audio Web site for the latest information
<http://www.yamaha.co.jp/product/proaudio/homeenglish/>.
Important Note
Whether you can actually use all the DS2416 functions that appear in the
manual will depend on your audio software.

4
Introduction
DS2416—Owner’s Manual
System Requirements
• IBM PC compatible PCI bus Windows 95 computer
• DS2416-compatible audio software
System Notes
The DS2416 can be used in any IBM PC-compatible PCI bus personal com-
puter running Windows 95. The DS2416 requires a single 5 V PCI expansion
bus slot, and cannot be used in 3.3 V PCI slots. It’s compliant with PCI ver-
sion 2.1, requires one IRQ (interrupt request), but no DMA (Direct Memory
Access). Since it’s a PCI card, IRQ settings are made automatically. PCI bus
speeds greater than 33 MHz are not supported.
Processor type, memory, and hard disk requirements are dependent on the
controlling software, not the DS2416. The supplied device driver requires a
few hundred kilobytes of disk space. Although the DS2416 supports 8-track
simultaneous recording and 16-track simultaneous playback, actual perfor-
mance will depend on the capabilities of your computer and audio software.
Compatible Software
Any software that supports Windows MME (Multimedia Extensions), includ-
ing the Windows 95 Media Player accessory, can be used with the DS2416 for
recording and playback. To use the mixing functions, however, requires soft-
ware that supports the DS2416 mixer. As of April 1998, the following software
companies are developing, or have already released software for the DS2416.
Please visit the following Web sites for more information.
•
C-Mexx
<http://www.c-mexx.com/>
•
Cakewalk
<http://www.cakewalk.com/>
•
Canam Computers
<http://www.canam-comp.fr/>
•
Emagic
<http://www.emagic.de/>
•
IQS (Innovative Quality Software)
<http://www.iqsoft.com/>
•
Musicator
<http://www.musicator.com/>
•
SEK’D
<http://www.sekd.com/CConsole/StudCcons.htm>
•
Sonic Foundry
<http://www.sfoundry.com/>
•
Steinberg
<http://www.steinberg.de/>
Audio software that doesn’t support all the features of the DS2416 can still use
a basic feature set. However, input and output patching is fixed, as shown in
the “Fixed Patchbay Diagram” on page 25. The Windows 95 Volume Control
can be used to set the stereo master fader and mute, and the level meters dis-
play the recording levels.

Features
5
DS2416—Owner’s Manual
Features
General
• PCI bus card (compliant with version 2.1)
• Support for Windows 95 MME (Multimedia Extensions)
• Plug and Play installation
• 5 onboard DSPs take the load off the computer’s main processor
• 2 analog inputs with 20-bit 128-times oversampling A/D converters
• 2 analog outputs with 20-bit 8-times oversampling D/A converters
• Stereo coaxial digital input and output (20- or 24-bit)
• Optional multi-channel analog and digital input and output options
Mixer
• 24 input channels, 8 bus outs, 6 aux sends (two feeding the onboard
effects processors), and a stereo output
• Input channels 21–24 function as effects returns for the onboard effects
• 4-band parametric EQ on all inputs channels and the stereo output
• Dynamics processors with reduction meters on all inputs channels and
the stereo output
• Two onboard effects processors with Yamaha ProR3/REV500 quality
• Input delay on input channels 1–20
• Signal level metering for all inputs and outputs
• Digital cascading of two DS2416 cards for 48-channel mixing
• 32-bit digital audio processing
Recorder
• 8-track simultaneous recording
• 16-track simultaneous playback
• Up to 32-bit recording and playback (software dependent)
• Sample-accurate synchronization between tracks
• External synchronization via controlling software

6
Connections
DS2416—Owner’s Manual
Connections
Rear
A
IN L, IN R
Analog IN L and IN R inputs feature phono jacks with a
nominal input level of –10 dBV. Analog to digital conversion
features 20-bit 128-times oversampling techniques. For best
performance use only shielded cables.
B
OUT L, OUT R
Analog OUT L and OUT R outputs feature phono jacks with
a nominal output level of –10 dBV. Digital to analog conver-
sion features 20-bit 8-times oversampling. For best perfor-
mance use only shielded cables.
C
D IN
This two-channel coaxial-type phono connection accepts
digital audio with a 24-bit maximum wordlength. Use con-
necting cables with a nominal impedance of 75 ohms.
D
D OUT
This two-channel coaxial-type phono connection outputs
digital audio with a 24-bit maximum wordlength. Use con-
necting cables with a nominal impedance of 75 ohms.
IN L
IN R
OUT L
OUT R
D IN
D OUT
1
2
3
4

Connections
7
DS2416—Owner’s Manual
Internal
A
SI (Serial In) connector
When two DS2416 cards are installed, this connector is connected to the “SO”
connector on the other card using the supplied 14-pin to 16-pin cable. Sound
cards that support the DS2416 can be connected directly to the mixer’s sub
inputs via this connector.
B
SO (Serial Out) connector
When two DS2416 cards are installed, this connector is connected to the “SI”
connector on the other card using the supplied 14-pin to 16-pin cable.
C
IO-A connector
This connector connects to the first optional AX44 Audio Expansion Unit.
D
IO-B connector
This connector connects to the second optional AX44 Audio Expansion Unit.
IO
A
B
1 2 3 4
SI
SO
IO-A
IO-B

8
Installing the DS2416
DS2416—Owner’s Manual
Installing the DS2416
The DS2416 installs into a PCI expansion slot and requires no special jumper
settings or interrupt settings.
See your computer’s manual for full details on installing PCI cards.
1
Turn off the computer and disconnect the power cord.
2
Remove the computer’s cover.
3
Choose an empty PCI slot for the DS2416, and remove the screw
from its expansion-slot cover.
To prevent static electricity from damaging the DS2416, touch a grounded
metal part of your computer, such as the power supply case, before handling
it.
4
Carefully align and insert the DS2416 into the PCI slot.
5
Secure the DS2416 using the screw removed previously.
6
Replace the computer’s cover.
7
Turn on your computer.
8
When the New Hardware Found dialog box appears, select “Driver
from disk provided by hardware manufacturer”, and then click OK.
9
When the Install From Disk dialog box appears, insert the driver
floppy disk into the floppy disk drive, and then click OK.
10
When the restart dialog box appears, restart your computer.
Important: The DS2416 is grounded via the expansion-card fixing screw, so
be sure to tighten it securely.

Testing the DS2416
9
DS2416—Owner’s Manual
Testing the DS2416
A test program is included with the DS2416 to make sure that the card, driver,
and DSPs are functioning correctly.
Installing the Test Program
1
Insert the supplied floppy disk into the floppy disk drive.
2
Double-click Setup.exe and follow the on-screen prompts.
The Test program and its associated files are installed.
Using the Test Program
1
From the Start menu, select Programs, DSP Factory, ds2416ck.exe.
2
When the Test program window appears, click the CHECK START
button to run the tests.
The Test program checks:
1. How many DS2416 cards are installed.
2. Whether the DS2416 drivers are installed
3. Whether the DSP chips are functioning correctly.
The test results appear as each test is completed. If all tests are successful, a
sine wave test tone can be produced through the OUT L, OUT R, D OUT, and
outputs 1 through 4 of any connected AX44s by clicking the test tone button.
If a test fails, follow the advice provided.
If the driver test fails again after restarting, try reinstalling the driver.
If the DSP test produces a “DSP ERROR” or “DSP NG” message, the DS2416
has a hardware problem and you should contact your Yamaha dealer.
3
Click the EXIT button to quit the Test program.

10
Wordclocks
DS2416—Owner’s Manual
Wordclocks
Unlike analog audio equipment, digital audio equipment must be synchro-
nized when digital audio is transferred from one device to another, otherwise,
the digital audio might not be read correctly and audible noise, glitches, or
clicks may occur. Synchronization is achieved using what’s called a wordclock,
which is a clock signal for synchronizing all the digital audio words in an
audio system. Note that wordclocks are not the same as SMPTE or MIDI
timecode, which are used to synchronize audio recorders, MIDI sequencers,
and so on. Wordclock synchronization refers to the synchronization of the
digital audio processing circuits inside each digital audio device.
In a typical digital audio system, one device acts as the wordclock master and
the other devices act as wordclock slaves, synchronizing to the wordclock
master. If the DS2416 is the only digital audio device in your system, no spe-
cial wordclock settings are required, as the DS2416 synchronizes to its own
internal wordclock. Add a DAT recorder or digital multitrack recorder, how-
ever, and you must decide which device to use as wordclock master and which
devices to use as slaves. Even when you’ve done this and configured your sys-
tem, it may sometimes be necessary to change the wordclock settings, such as
when recording from a DAT or CD player.
Wordclocks run at the same frequency as the sampling rate. The DS2416 gen-
erates its own wordclock at 44.1 kHz (the industry-standard sampling rate for
music CDs) or 48 kHz and can be used as wordclock master. Alternatively, it
can be used as a wordclock slave synchronized to an external wordclock of
between 30.08 kHz and 50.88 kHz (32 kHz –6% to 48 kHz +6%). Converting
the sampling rate of digital audio is a complicated process, so it’s best to use
the 44.1 kHz sampling rate, especially if your work is destined for CD distri-
bution.
Wordclock signals can be distributed via dedicated cables or derived from
standard digital audio connections, such as the D IN and D OUT connections
on the DS2416. With Coaxial digital audio connections, a wordclock signal is
transmitted even when no audio signal is present. The DS2416 can also trans-
mit and receive wordclock signals via its SI, SO, IO-A, and IO-B connectors.
In a system where all devices share a common wordclock, it’s important that
all devices be turned on even when they’re not being used. Turn on the word-
clock master first, and then the slaves. When shutting down the system, turn
off the slaves first, and then the master. Before commencing with a recording
session, make sure that all wordclock slaves are synchronized to the master.
Some devices have front panel indicators to show when they are wordclock
synchronized. Refer to the instructions for each device.

Wordclocks 11
DS2416—Owner’s Manual
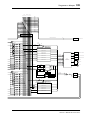
Recording Digitally to the DS2416
In this example, a DAT deck is connected to the DS2416 D IN connector for
digital recording. The DS2416 works as wordclock slave, deriving its word-
clock from the D IN connection, and the DAT works as wordclock master.
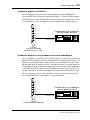
Recording Digitally to DAT
In this example, the D OUT connector on the DS2416 is connected to the dig-
ital input of a DAT recorder for digital mixdown recording. The DS2416
works as wordclock master and the DAT works as wordclock slave. When the
digital input on the DAT recorder is selected as the recording source, the DAT
should automatically synchronize to the wordclock signal coming from the
DS2416. On some DAT recorders, the wordclock source may have to be set
separately. Refer to the instructions supplied with your DAT recorder.
IN L
IN R
OUT L
OUT R
D IN
D OUT
DAT
00.00.00.00
Digital Out
DAT recorder
(wordclock master)
DS2416
(wordclock slave
Source = D IN)
IN L
IN R
OUT L
OUT R
D IN
D OUT
DAT
00.00.00.00
Digital In
DAT recorder
(wordclock slave)
DS2416
(wordclock master)

12 Digitally Cascading DS2416 Cards
DS2416—Owner’s Manual
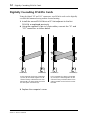
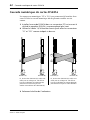
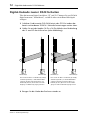
Digitally Cascading DS2416 Cards
Using the digital “SI” and “SO” connectors, two DS2416 cards can be digitally
cascaded for common busing and 48-channel mixing.
1 Install the second DS2416 into a PCI slot adjacent to the first
DS2416, as explained previously.
2 Using the supplied 14-pin to 16-pin cables, connect the “SI” and
“SO” connectors as shown below.
3 Replace the computer’s cover.
DS2416 (A) DS2416 (B)
I
O
I
O
DS2416 (A) DS2416 (B)
I
O
In this example, the buses of DS2416
(A) and (B) are linked together for 48-
channel mixing. Individual buses from
DS2416 (B) can alternatively be fed to
the sub inputs of DS2416 (A).
In this example, the buses of DS2416
(A) and (B) are linked together for 48-
channel mixing. Individual buses from
either DS2416 can be fed to the other
DS2416.

DS2416 Q&A (Questions & Answers) 13
DS2416—Owner’s Manual
DS2416 Q&A (Questions & Answers)
Q What’s a DSP?
A A DSP, or Digital Signal Processor is a processor optimized for
real-time digital data processing. The DS2416 features the same
DSP as the Yamaha 02R and 03D digital mixing consoles and
ProR3 and REV500 effects processors.
Q At what wordlength is digital audio processed?
A The EQ features a 44-bit data path, 32-bit coefficient, and 54-bit
accumulator. All other mixer sections feature a 32-bit data path,
24-bit coefficient, and 42-bit accumulator.
Q Does the DS2416 have any onboard memory?
A Yes, 3 megabytes, which is used for input, and effects delays.
Q What is the available recording time?
A This depends on the software, selected wordlength, and hard disk
space. In general, two channels of 16-bit digital audio use 10.6
MB/min.
Q How do I synchronize the DS2416 to MIDI Clock, MTC, or SMPTE
timecode?
A If the software and timecode interface support external timecode,
so does the DS2416.
Q Can DS2416 mixer functions be controlled via MIDI?
A If the controlling software supports this, yes.
Q How good are the onboard effects processors?
A As good as those used in the Yamaha ProR3 and REV500 effects
processors.
Q Can the DS2416 be used simultaneously with a Sound Blaster or
Korg 1212 I/O card?
A Yes.

14 Troubleshooting
DS2416—Owner’s Manual
Troubleshooting
Trouble Advice
The DS2416 does not work?
Make sure that the DS2416 is inserted in the
PCI bus slot correctly.
Make sure that the DS2416 input and outputs
are correctly assigned using the controlling
software.
In older computers, some PCI slots may not
function as the bus master, and the DS2416 will
not work in such slots. See your computer’s
manual for more details.
Some PCI cards may conflict with the DS2416.
Try removing cards, or swapping slots with the
DS2416.
A low-level hum can be heard?
The DS2416 is grounded via the expan-
sion-card fixing screw, so be sure to tighten it
securely.

Effects Programs 15
DS2416—Owner’s Manual
Effects Programs
The DS2416 provides the following effects programs. Detailed effects param-
eters are shown on page 149.
Reverb-type Effects
Delays
Type Description
REVERB HALL Reverb simulating a large space such as a concert hall.
REVERB ROOM Reverb simulating the acoustics of a smaller space than REVERB HALL.
REVERB STAGE Reverb designed with vocals in mind.
REVERB PLATE
Simulation of a metal-plate reverb unit, producing a feeling of
hard-edged reverberation.
EARLY REF.
An effect which isolates only the early reflection (ER) component from
reverberation. A flashier effect than reverb is produced.
GATE REVERB A type of ER designed for use as gated reverb.
REVERSE GATE A reverse-playback type ER.
Type Description
MONO DELAY
Mono delay with simple operation. Use when you don't need to use
complex parameter settings.
STEREO DELAY Stereo delay with independent left and right.
MOD.DELAY Mono delay with modulation.
DELAY LCR Three-tap delay (L, C, R).
ECHO
Stereo delay with additional parameters for more detailed control. The
signal can be fed back from left to right, and right to left.

16 Effects Programs
DS2416—Owner’s Manual
Modulation-type Effects
Guitar Effects
Dynamic Effects
Type Description
CHORUS Three-phase stereo chorus.
FLANGE The well-known flanging effect.
SYMPHONIC
A Yamaha proprietary effect that produces a richer and more complex
modulation than chorus.
PHASER Stereo phaser with 2–16 stages of phase shift.
AUTO PAN An effect which cyclically moves the sound between left and right.
TREMOLO Tremolo
HQ.PITCH
(Effect 2 only)
Only one note is pitch-shifted, but a stable effect is produced.
DUAL PITCH Stereo pitch shift with left and right pitches set independently.
ROTARY Simulation of a rotary speaker.
RING MOD.
An effect that modifies the pitch by applying amplitude modulation to
the frequency of the input.
MOD.FILTER An effect which uses an LFO to modulate the frequency of the filter.
Type Description
DISTORTION Distortion
AMP SIMULATE Guitar Amp Simulator
Type Description
DYNA.FILTER Dynamically controlled filter.
DYNA.FLANGE Dynamically controlled flange.
DYNA.PHASER Dynamically controlled phase shifter.

Effects Programs 17
DS2416—Owner’s Manual
Combined Effects
Type Description
REV+CHORUS Reverb and chorus in parallel
REV->CHORUS Reverb and chorus in series
REV+FLANGE Reverb and flange in parallel
REV->FLANGE Reverb and flange in series
REV+SYMPHO. Reverb and symphonic in parallel
REV->SYMPHO. Reverb and symphonic in series
REV->PAN Reverb and auto-pan in parallel
DELAY+ER. Delay and early reflections in parallel
DELAY->ER. Delay and early reflections in series
DELAY+REV Delay and reverb in parallel
DELAY->REV Delay and reverb in series
DIST->DELAY Distortion and delay in series

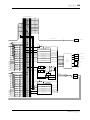
18 Block Diagram
DS2416—Owner’s Manual
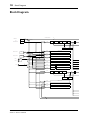
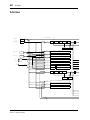
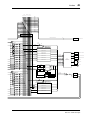
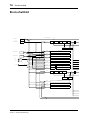
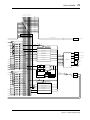
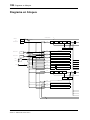
Block Diagram
SAME AS CH1
CH1
CH2-8
SAME AS CH1
CH9-12
SAME AS CH1
CH13-16
SAME AS CH1
CH17
SAME AS CH1
CH18
SAME AS CH1
CH19
SAME AS CH1
CH20
A/D
CHANNEL
METER
ON
REDUCTION
METER
Signal
Pre
Post
SAME AS CH21
CH21
SAME AS CH21
CH22
SAME AS CH21
CH23
CH24
STEREO
MASTER
CASCADE IN(16ch)
SUB IN(8ch)
PCI
PLAYBACK(16ch)
IO-B
IO-A
PCI
SI
A IN L
A IN R
D IN
IO-A IN(4 or 8ch)
IO-B IN(4 or 8ch)
SERIAL IN
16 or 8
16
8
16
4 or 8
4
2
2
2
2
7
4
4
4
4
4 or 8
4
4 4
8
7
78
4
4
4
4
4
DC-CUT
ATT/PHASE
4BAND
PEQ
DYNAMICS
DE-EMPHASIS
DE-EMPHASIS
CHANNEL
METER
ON
REDUCTION
METER
Signal
Pre
Post
DC-CUT
ATT/PHASE
4BAND
PEQ
DYNAMICS
DELAY
BALANCE
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
Pagina se încarcă ...
-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
-
 29
29
-
 30
30
-
 31
31
-
 32
32
-
 33
33
-
 34
34
-
 35
35
-
 36
36
-
 37
37
-
 38
38
-
 39
39
-
 40
40
-
 41
41
-
 42
42
-
 43
43
-
 44
44
-
 45
45
-
 46
46
-
 47
47
-
 48
48
-
 49
49
-
 50
50
-
 51
51
-
 52
52
-
 53
53
-
 54
54
-
 55
55
-
 56
56
-
 57
57
-
 58
58
-
 59
59
-
 60
60
-
 61
61
-
 62
62
-
 63
63
-
 64
64
-
 65
65
-
 66
66
-
 67
67
-
 68
68
-
 69
69
-
 70
70
-
 71
71
-
 72
72
-
 73
73
-
 74
74
-
 75
75
-
 76
76
-
 77
77
-
 78
78
-
 79
79
-
 80
80
-
 81
81
-
 82
82
-
 83
83
-
 84
84
-
 85
85
-
 86
86
-
 87
87
-
 88
88
-
 89
89
-
 90
90
-
 91
91
-
 92
92
-
 93
93
-
 94
94
-
 95
95
-
 96
96
-
 97
97
-
 98
98
-
 99
99
-
 100
100
-
 101
101
-
 102
102
-
 103
103
-
 104
104
-
 105
105
-
 106
106
-
 107
107
-
 108
108
-
 109
109
-
 110
110
-
 111
111
-
 112
112
-
 113
113
-
 114
114
-
 115
115
-
 116
116
-
 117
117
-
 118
118
-
 119
119
-
 120
120
-
 121
121
-
 122
122
-
 123
123
-
 124
124
-
 125
125
-
 126
126
-
 127
127
-
 128
128
-
 129
129
-
 130
130
-
 131
131
-
 132
132
-
 133
133
-
 134
134
-
 135
135
-
 136
136
-
 137
137
-
 138
138
-
 139
139
-
 140
140
-
 141
141
-
 142
142
-
 143
143
-
 144
144
-
 145
145
-
 146
146
-
 147
147
-
 148
148
-
 149
149
-
 150
150
-
 151
151
-
 152
152
-
 153
153
-
 154
154
-
 155
155
-
 156
156
-
 157
157
-
 158
158
-
 159
159
-
 160
160
-
 161
161
Yamaha DS2416 Manualul proprietarului
- Categorie
- Mixere audio
- Tip
- Manualul proprietarului
în alte limbi
- Türkçe: Yamaha DS2416 El kitabı
- français: Yamaha DS2416 Le manuel du propriétaire
- čeština: Yamaha DS2416 Návod k obsluze
- русский: Yamaha DS2416 Инструкция по применению
- English: Yamaha DS2416 Owner's manual
- polski: Yamaha DS2416 Instrukcja obsługi
- Deutsch: Yamaha DS2416 Bedienungsanleitung
- 日本語: Yamaha DS2416 取扱説明書
- italiano: Yamaha DS2416 Manuale del proprietario
- español: Yamaha DS2416 El manual del propietario
- svenska: Yamaha DS2416 Bruksanvisning
- dansk: Yamaha DS2416 Brugervejledning
- português: Yamaha DS2416 Manual do proprietário
- Nederlands: Yamaha DS2416 de handleiding
Lucrări conexe
-
Yamaha AX16 Manualul proprietarului
-
Yamaha AX44 Manualul proprietarului
-
Yamaha SW1000XG Manualul proprietarului
-
Yamaha ProR3 Manual de utilizare
-
Yamaha VA-10 Manualul proprietarului
-
Yamaha AR-2500 Manualul proprietarului
-
Yamaha MY8-AD96 Manual de utilizare
-
Yamaha UD-FD01 Manualul proprietarului
-
Yamaha SREV1 Manualul proprietarului
-
Yamaha DME32 Manualul proprietarului

































































































































































